What are Serial Ports used for?
Following are some of the uses of COM ports in business and industry.
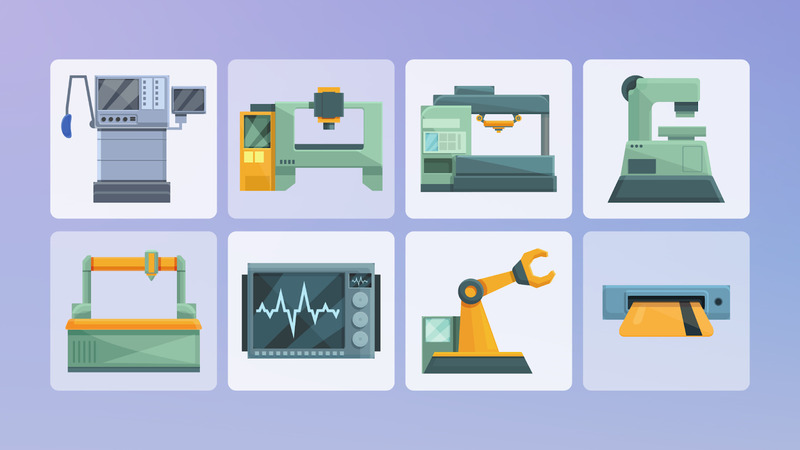
- Industrial automation: COM ports are necessary to support industrial automation by facilitating communication between PLCs, sensors, controllers, and other automated devices. Serial ports are used to provide human-machine interfaces (HMIs) so operators can interact with industrial devices and manage machine operations.
- Fire control panel remote access: Modern fire safety systems rely on hardware and software to identify potential issues and generate alerts to essential personnel. Remote monitoring systems employ serial devices connected to centralized control panels.
- Medical Devices: A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a software solution used to automate workflows and tracking for improved efficiency. The system communicates with lab instruments through serial ports.
- Consumer Electronics: Many consumer devices utilize COM ports to furnish simple and accurate communication. Examples include barcode scanners, measuring equipment, and GPS devices.
- Farm management: Many types of equipment used on modern farms communicate via serial ports. A wide range of serial devices are used to help control pollution, monitor livestock health, automate irrigation activities, and perform many other farm-related operations.
Note: If you need to work with
Serial port over Ethernet or any other Network (TCP/IP, LAN, WAN) use the software from Electronic Team. Serial to Ethernet Connector is a simple solution to share COM port.
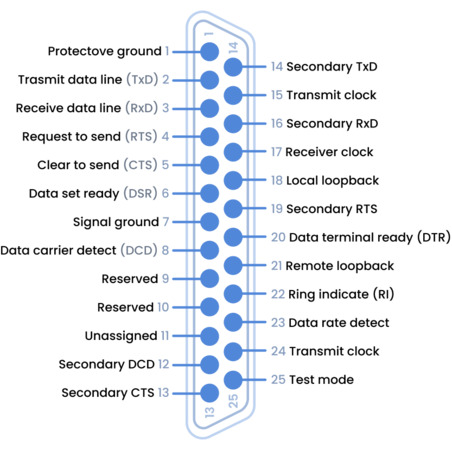
The Role of COM Ports in Serial Communication
An understanding of COM ports helps you manage and optimize serial devices and systems. This knowledge can be used to efficiently configure industrial equipment, troubleshoot communication issues between devices and computers, or streamline network communication. Knowing how COM ports work is also useful when interacting with consumer electronics or serial medical devices.
COM ports are an essential component of serial communication. By transmitting a single bit of data at a time, serial communication provides enhanced reliability compared to parallel communication methods. The steady flow of data furnished by COM ports is vitally important for supporting industrial, medical, and other systems requiring high data reliability.